Market Segmentation
Understanding your customer is the first step to winning them over.
Market segmentation is a powerful strategy that enables businesses to tailor their marketing efforts to specific consumer groups. By dividing a broad market into smaller segments based on shared characteristics, companies can create personalized campaigns that resonate more deeply with their target audience, enhancing engagement and conversion rates. Imagine a clothing retailer sending promotions based on a customer’s past purchases or preferences—this is the power of market segmentation.
Market segmentation requires ongoing analysis and adaptation. As consumer behaviors and market trends evolve, businesses must revisit their segmentation strategies to ensure alignment with their audience’s needs.
Criteria for Effective Market Segmentation
To be effective, market segments must be:
Identifiable: Each segment should have distinct characteristics that make it stand out from the rest of the market.
Accessible: Segments should be easy to target and reachable with a marketing plan.
Substantial: Segments must be large enough to be profitable and viable for the long term.
Measurable: The size, profit, and potential of each segment should be quantifiable.
Actionable: Organizations must be able to develop relevant and attractive programs for each segment.
Types of Market Segmentation
Marketers can develop their own methods based on their company’s outlook. Common types of market segmentation include:
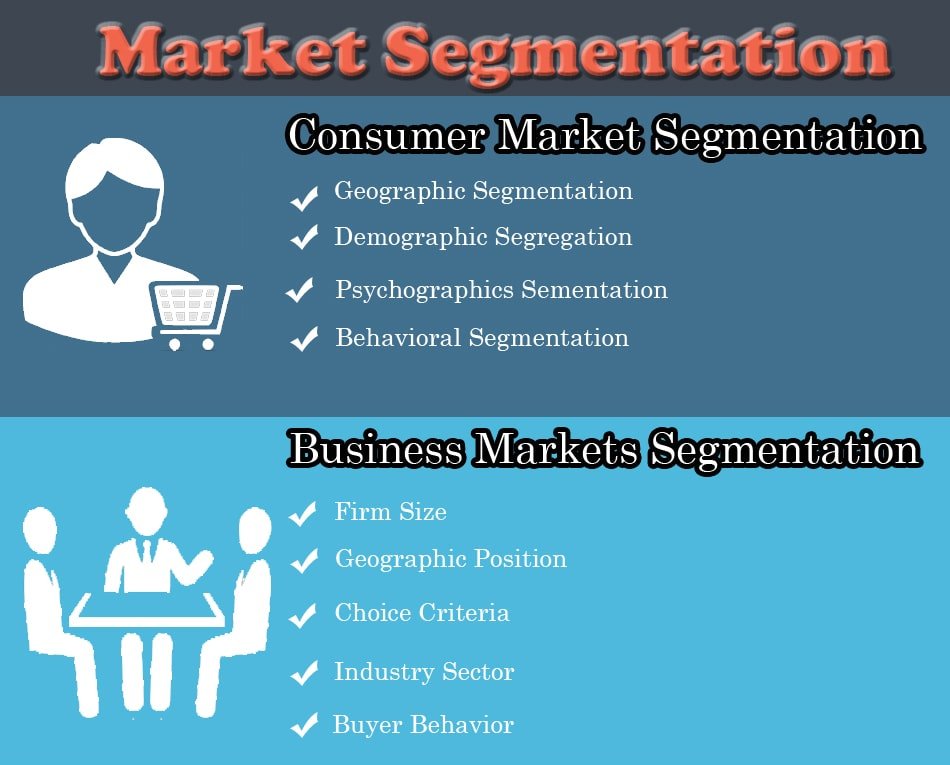
Consumer Market Segmentation
Geographic Segmentation: Dividing the market into geographic units, such as countries, regions, and cities, allowing for tailored marketing programs.
Demographic Segmentation: Using variables like age, income, family size, and life cycle to understand consumer needs and wants.
Psychographic Segmentation: Grouping buyers based on psychological traits, lifestyle, or values.
Behavioral Segmentation: Dividing buyers based on their knowledge, attitudes, use, and response to a product.
Business Market Segmentation
Firm Size: Considering factors like the number of employees and market share to understand buying rates and processes.
Geographic Position: Using geographic criteria to identify sales territories.
Choice Criteria: Segmenting based on the specific products customers are looking for.
Industry Sector: Grouping businesses by their activities, such as manufacturing or retail.
Buyer Behavior: Creating segments based on usage rate, loyalty, and order size.
Benefits of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation offers numerous benefits for both customers and marketing organizations, including:
Better Product Strategy: Helps in creating and reviewing products to better suit the market.
Effective Pricing Strategy: Allows for setting prices based on different market segments’ perceptions.
New Marketing Opportunities: Identifies new market segments, leading to increased market share.
Cost-Efficiency: Saves time, money, and resources by targeting the right audience.
Higher Customer Satisfaction: Tailors the marketing mix to meet the specific needs of a segment.
Adequate Market Plan: Gathers sufficient information about customers’ unique needs.
Assist in Distribution Strategies: Helps choose the right distribution strategy for different market segments.
Design Targeted Ads: Creates effective ad campaigns based on customer preferences.
Proper Resource Usage: Focuses resources on profitable areas, minimizing costs on unproductive sectors.
Conclusion
Market segmentation is a vital strategy for businesses looking to enhance their marketing efforts and connect more deeply with their target audience. By identifying distinct segments and tailoring marketing strategies accordingly, companies can achieve higher engagement, increased customer satisfaction, and sustainable growth. As market trends and consumer behaviors continue to evolve, ongoing analysis and adaptation are essential to stay competitive and foster long-term customer relationships.