Parenting Styles and Their Influence on Child Self-esteem
The way parents interact with their children can have a lasting impact on their self-perception.
Parenting styles significantly contribute to the self-esteem of a child, affecting their emotional and psychological well-being. Being aware of the styles and their effects can help parents promote healthier self-esteem in children.
Overview of Parenting Styles
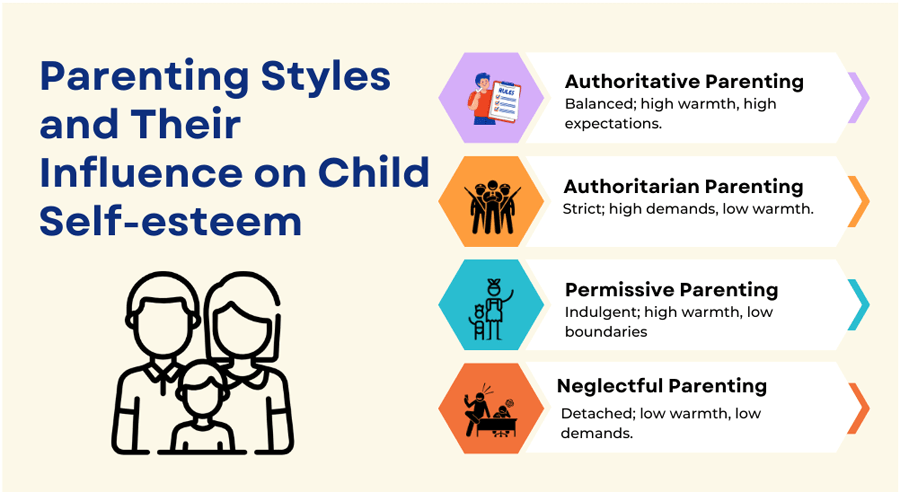
Parenting styles are generally divided into four fundamental types:
Authoritative Parenting
Authoritative parenting is marked by high responsiveness and high demands. Authoritative parents are supportive and nurturing, but they also set clear expectations and enforce consistent rules. This balanced approach helps children understand boundaries while feeling secure and loved.
Positive Effects
Children raised by authoritative parents often exhibit high self-esteem. They benefit from emotional warmth, consistent support, and open communication. This supportive environment enables children to explore themselves fearlessly and become resilient. These children, research shows, have better social skills and less anxiety and aggression. For example, a child who can freely discuss their emotions and is given positive feedback is most likely to develop into an emotionally intelligent and self-assured individual.
Negative Effects
Overall, authoritarian parenting is linked to positive results, yet overemphasis on expectations, even within the framework of love, might lead to pressure. When parents are overly demanding or critical, children can become anxious or fearing to disappoint their parents.
Authoritarian Parenting
Authoritarian parenting is characterized by strict rules, high demands, and low responsiveness. These parents exercise discipline and demand obedience without much warmth or emotional support. Communication is often one-way with little room for discussion or compromise.
Positive Effects
In some cases, children raised in authoritarian households may develop a strong sense of responsibility and discipline. The clear rules can provide structure, which can be reassuring for some children. For example, a child who is trained to follow a structured daily routine can perform well at school and be well organized.
Negative Effects
More commonly, authoritarian parenting decreases the self-esteem of a child. The lack of warmth and mere control can generate anxiety and feelings of inadequacy. Children will internalize criticism, develop a negative self-esteem, and feel loved only for performance and obedience. This will stifle their ability to make independent decisions and render social interaction difficult. For instance, a child who is repeatedly criticized for making minor mistakes will become overly self-critical and fearful of attempting new things.
Permissive Parenting
Permissive parents are warm and nurturing, providing affection and warmth but having few rules or limits. They attempt to avoid conflict and permit children to make their own decisions with little guidance.
Positive Effects
Children with permissive parents are likely to feel loved and accepted, and this can promote self-esteem. Being allowed the freedom to find their interests and make their own choices can stimulate creativity and independence. For example, a child who is allowed to pursue their interests without close monitoring can become highly developed in personal interests and confidence.
Negative Effects
However, the lack of structure and guidance can cause problems. Children may struggle with self-regulation, responsibility, and understanding limits. This lack of limits can result in a false sense of entitlement and rage when they are faced with actual consequences in the world. As a result, these children may actually have lower self-esteem due to the lack of explicit guidance and support. For instance, a child who is never held responsible for their actions can fail in school and social settings, lacking control of themselves and doubting their ability.
Neglectful Parenting
Neglectful parents are unresponsive and undemanding, and they are detached from the child’s needs and uninvolved in their lives. The lack of attention and support can lead to children feeling neglected and irrelevant.
Positive Effects
In a few exceptional instances, children who are raised in neglectful households become very independent and self-reliant as they learn to repair things on their own. But these are exceptions rather than the rule.
Negative Effects
Neglectful parenting can be very harmful to a child’s self-esteem. Children typically feel unwanted, insecure, and worthless. Inadequate emotional support and guidance can lead to poor emotional regulation, behavior problems, and difficulty forming healthy relationships. Adolescents raised by neglectful parents are more likely to have greater substance use, delinquency, and poor academic performance. For example, a child who consistently feels ignored will either behave badly to receive attention or retreat and believe they do not deserve love and care.
Conclusion
Parents are encouraged to adopt approaches that promote emotional warmth, boundary setting, and open communication. By creating a warm but structured environment, parents can help their children develop into confident, well-adjusted individuals who can confront life’s challenges with resilience and self-confidence. With an understanding of these dynamics, parents can make rational choices that support their child’s emotional and psychological development, clearing the path for a happy and successful future.