Economic Inequality
Did you know the top 1% now owns more wealth than the bottom 50% combined?
The general definition of economic inequality is the disparity, in income or wealth, among various groups in a society.
Across all societies, economic inequality is the critical factor affecting human life. It is not just statistical figure; it shows how lives are shaped by wealth disparity and opportunity deprivation.
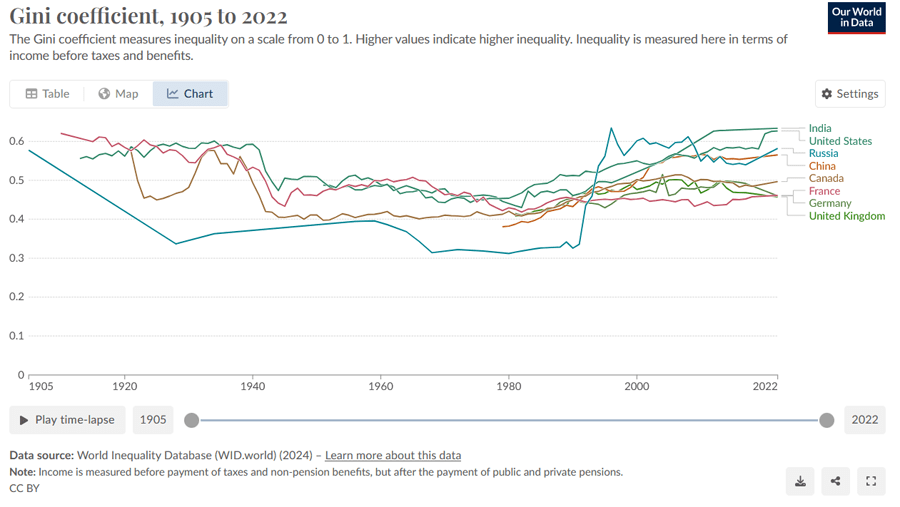
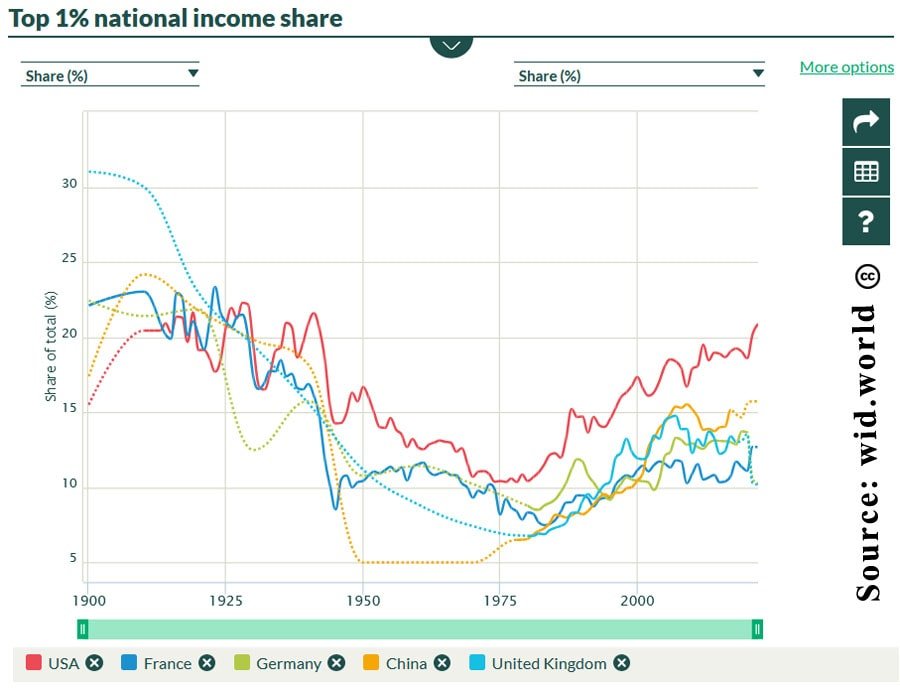
Source: https://ourworldindata.org/economic-inequality
The line drawn between the rich and the poor keeps widening, throwing millions into the fight just to survive. This is indeed base reality for some, and this is one issue we cannot afford to neglect. As a society, we have to come together to tackle the root causes of economic inequality and work toward a brighter future for all.
Causes of Economic Inequality

Globalization
Increased trade through globalization can actually widen economic inequality. It raises competition for low-skilled jobs in wealthier nations, thereby pulling down the wage levels for such jobs. Some economists believe that 5% to 15% of that increasing inequality is attributable to globalization. Yet others believe technological advancement plays a much larger part.
Technological Change
Low-skilled jobs can be performed by machines, so that there can be little work opportunity for low-skilled persons in affluent countries. This drives a further gap between income earners of high skills and those of low skills.
Historical Factors
Enduring legacies of systemic racism and past discriminatory practices give continuity to economic inequalities. For instance, slavery and the Jim Crow laws in the United States made deep imprints on the black population in terms of economic opportunities and wealth accumulation. Such historical background helps to give continuation to economic inequality.
Inequality of Opportunity
Disparities in education, resource access, and social mobility can result in huge economic inequalities. For example: various types of inequality in land holdings, might encourage high inflation rates, and consequently cause income disparities in developing countries.
Economic Policies
Redistributive fiscal, labor market regulation, and other standard domestic policy instrument can have an effect on economic equality. The lack of a strong social safety net and stagnating real wages tend to intensify income inequality incidences among different countries.
Natural Disaster
It can worsen economic disparities because they usually affect vulnerable communities which lack resources and infrastructure more severely than areas that are generally better off.
Inflation and Stagnant Wages
In the case of high inflation along with stagnant wages, this will cut the purchasing power especially for low-income households. The best-case example is that across the U.S. the federal minimum wage has not been raised since 2009 and many minimum wage earners face significant hardships in meeting such essential expenses.
Social and Economic Factors
Various factors further widen economic inequalities, such as long-term unemployment, low salaries, limited chances for education, and homelessness. For example, long-term unemployment is associated with psychological disorders, debt, and deteriorating health conditions.
Consequences of Economic Inequality
Social and Political Tensions
It can foster social discrimination and distrust in institutions and result in political instability. It has been linked with an increase in crime rates, lower civic participation, and generous support for authoritarian or populist movements in society.
Health Disparities
Low income has direct correlation with poor health and mental condition, increased mortality rates, chronic illnesses, and lower life expectancy because of limited access to health facilities and higher levels of stress.
Economic Growth
Extreme inequality hinders economic growth by constraining investment in human capital, reducing social mobility, and inducing political instability. Some studies also find a negative relationship between inequality and long-term economic growth.
Access to Services
Economic inequality influences equal access to important services, including education, health, and housing.
Addressing Economic Inequality

Increase the Minimum Wage
Increasing the minimum salary can significantly reduce poverty and promote economic security among low-paid employees. Studies suggested that higher wages do not always result in lower employment levels, but they may create a net positive contribution to actual national income.
Build Assets for Poor Families
Policies to promote savings rates and reduce asset accumulation costs for working and middle-class households can improve economic security for struggling families. Examples would include auto-enrollment in retirement accounts followed by savings incentives, such as federal matching for retirement accounts.
Investment in Education
Access to quality education is important for reducing economic inequality. It includes undertaking policies or measures that widen access to education by indigent students, increasing funding for schools in marginalized areas.
Progressive Tax
Tax policy must aim to redistribute wealth and income more equitably. This can involve raising tax rates for rich individuals and introducing progressive tax systems, which charge higher rates for higher incomes.
Social Welfare Programs
The government may alleviate inequity through tax and income support programs such as welfare, free healthcare, and food stamps. These initiatives would help to reduce sudden negative impact cause by economic shocks t effects and provide safety nets for vulnerable populations.
Promote Inclusive Economic Growth
Policies should be judged by its ability to ensure economic growth on every sector of the society. This includes access to higher value employment plus implementing equal opportunity to employment and enhancing social safety nets.
Land Redistribution
Changes in land ownership might help to some extent reduce economic inequality. Such policies that promote the fair distribution of land would enable low-income households to have a stake in property ownership, thus increasing the income status of that population segment.
Improve Access to Financial Services
Access to financial services, especially banking and credit, is actually empowering low-income households to manage their incomes and accumulate wealth.
Conclusion
Probably economic inequality is one of the most difficult economic problems to solve. We know that unequal economic status leads to less cooperation, health, and economic growth.
There are several policies nevertheless which politicians can bring to the table to set up conditions to distribute resources more equitably in between rich and poor. Of course, raising minimum wages, expanding safety nets, and funding initiatives provide opportunity and resource access for low-income families.
Economic inequality is more than a policy issue. We have to create inclusive society that works for everyone. This is the challenge we face to create a better tomorrow. So, single effort is not enough, we need to work collectively to eliminate economic inequality from roots.