Building a Strong Business Plan
A well-crafted business plan is not just a document; it is your roadmap to success.
One of the most significant steps a potential entrepreneur takes while entering a business is writing a highly feasible business plan. A business plan, better if written, guides you through everything in the path of success step by step. It outlines objectives and strategies of the business firm, resources expected to achieve desired goals. In this paper, let’s develop an effective business plan that may introduce a pathway leading to success.
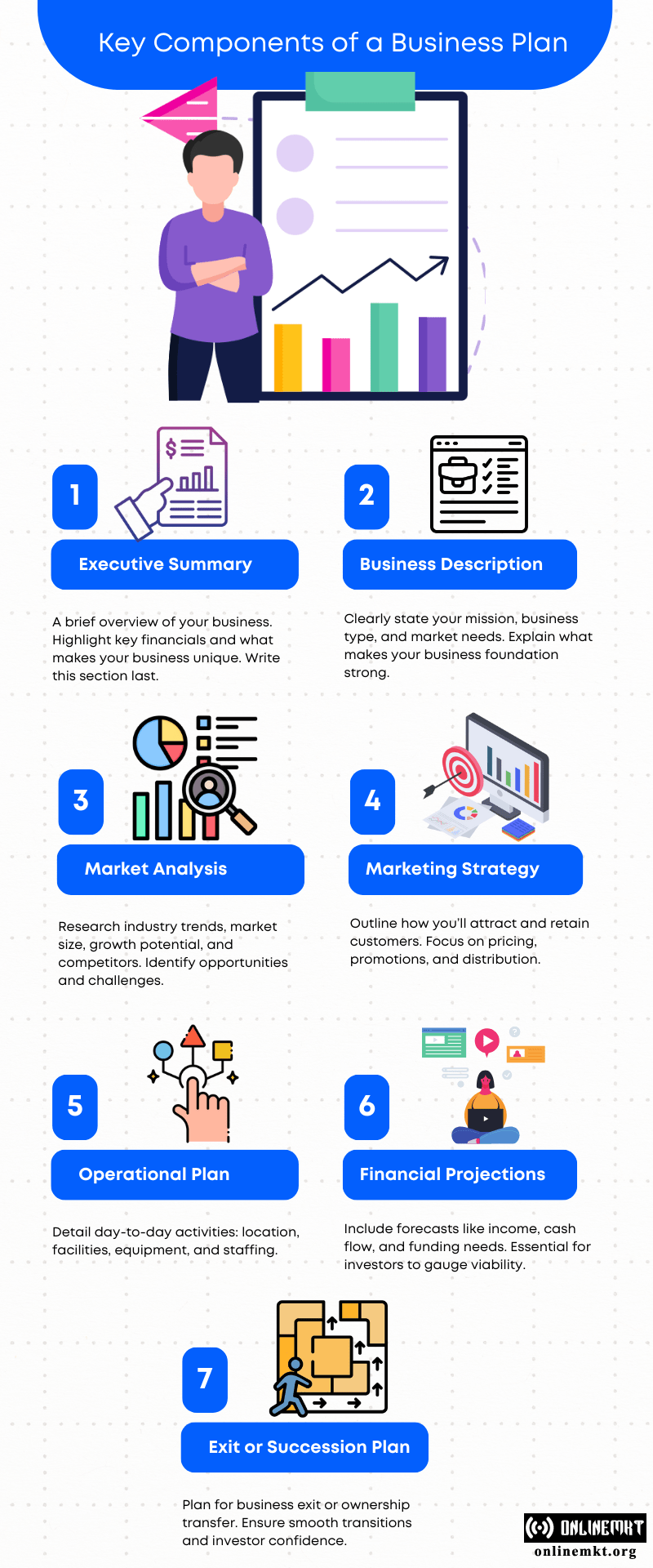
Key Components of a Business Plan
A typical business plan includes several essential sections that together form the blueprint of your business:
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary This section summarizes your entire business plan in a brief overview. It should concisely capture the essence of your business concept, key financial features, and describe your current business position. This section appears first in the plan, but in reality, it is often best written last because it reflects the critical points discussed in all the other sections.
Imagine you are pitching your startup to venture capital. The Executive Summary is your first and maybe final impression-a snapshot of what is unique about your business and why anyone should invest in it.
Business Description
This section thoroughly explains your business in detail. Here is where you state the mission of the company, explain what the business enterprise represents, and the markets you will look to meet those needs in. Through the use of description, you are just showing readers the foundation of your business.
If your business, for instance, is a sustainable clothing line, then your description will include your use of eco-friendly materials, ethical manufacturing, and your target market of environmentally conscious consumers.
Market Analysis
Market research is necessary for the understanding of the business environment in which your venture is supposed to work. This may include industry trend research, assessment of the size of the market, determination of growth potential, and who your target audience is. A good market analysis will reveal some opportunities but help you prepare for potential challenges in advance.
For instance, in the case of a technology start-up, market analysis might reveal a growing demand for the need of remote work solutions, therefore defining immediately both the target market and its competitors in the provision of such needs.
Marketing Strategy
This section maps out your game plan for reaching and retaining your customers. In this section is where you establish price, promotion, and place. If there is a refined marketing strategy laid out, the product or service will reach targeted audience effectively.
A new restaurant might identify social media campaigns, offering various daily deals along with their other specialty offerings.
Operational Plan
The Operational Plan outlines the operations needed to run your business. This section addresses your business location, the type of facilities you will occupy, what type of equipment you will need, and the personnel you will need to carry on your operations.
In an ecommerce business, for example, the operational plan would include discussions on warehouse management right down to order fulfillment and customer service protocols.
Financial Projections
Financial projections represent an essential category of your business plan. This section includes detailed forecasts, such as income statements, cash flow projections, and balance sheets. Besides this, it should cover your funding needs and sources of finance. This is the section on which investors and lenders will put the most attention to analyze whether your business is viable or not from a financial perspective.
A venture capital-seeking startup may produce a five-year financial forecast that outlines how early investments are to be deployed in scaling the operation and generating profits.
Exit or Succession Plan
The Succession or Exit Plan is usually the neglected area in business planning. It describes how one intends to exit the business or ownership and, therefore, long-term planning in nature and may be used in building investor confidence. Whether one intends to sell the business, pass it to a family member, or go public, one must have an exit strategy in place for any smooth transition to take place.
A family-owned business may include a succession plan that outlines how ownership will be transferred to the next generation.
Importance of a Business Plan
A business plan is not just a document; it is a key to success. Here’s why:
Clarifies Your Vision
Writing a business plan forces one to articulate the business idea clearly, besides assessing the feasibility of the idea. It really is a forcing function to really think things through critically about the business model, market strategy, and overall vision.
Attracts investors
The well-planned business plan will attract funding. Investors like to see a clear, detailed plan that outlines how their investment is to be utilized and the potential returns they expect.
Guides Decision-Making
It shows your business strategically in the right direction and thus enables you to make better, more calculated decisions while undertaking a rough journey for managing the business. It puts your business on the right track for the accomplishment of the predefined goals.
Recognizes Risks and Opportunities
Your business plan, through great research and analysis, identifies opportunities and risks likely to face you in the market. Such foresight puts you in a position to be ready for challenges or to capitalize on opportunities
How to Write a Good Business Plan
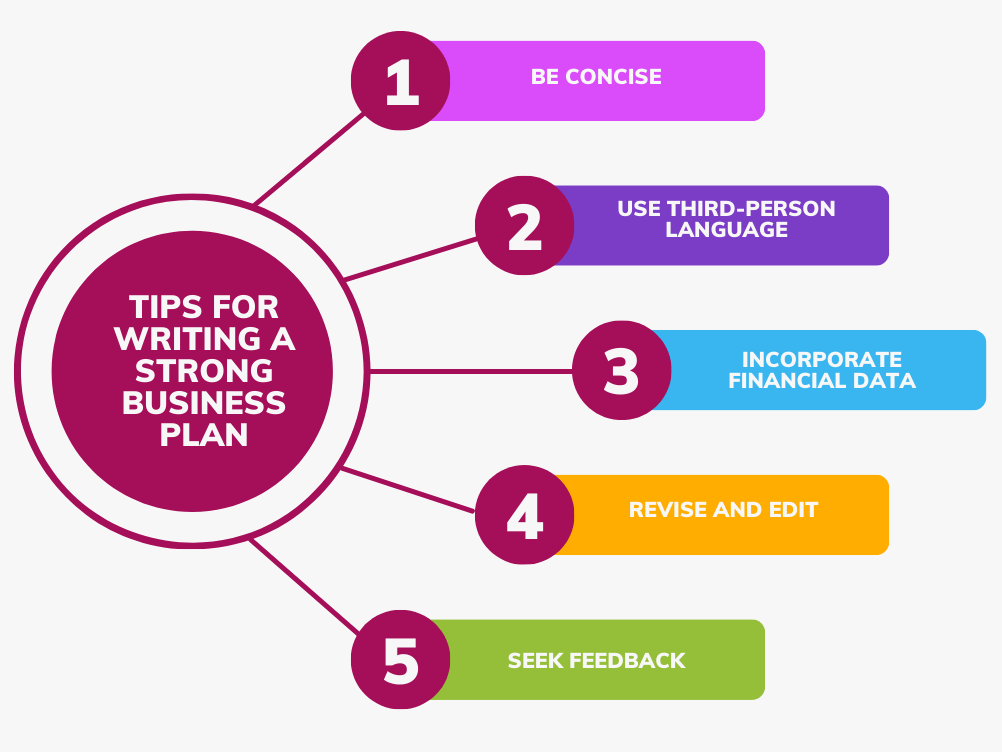
Be Brief
Your business plan does not have to be long. Make your plan concise, clear, and simple with no ambiguity in any section.
Write in Third-Person
Your business plan should be in the third person. This helps you to be professional and objective. In this way, you can stay focused on the business rather than yourself.
Include Financial Information
While the narrative descriptions are significant, the inclusion of financial projections is essential. Present data with charts and tables in a very clear and appealing manner.
Revision and Editing
Once you have finished drafting, make sure to go back and revise and edit your work carefully. You can read it backwards, to catch mistakes, and check for logical flow of sentences in each paragraph.
Gather Feedback
Let others like mentors, peers, or experts in business take a look at your plan. Their advice would help you to beautify business plan and give you a glimpse of possible mistakes in the plan.
Conclusion
Writing a good business plan requires detailed research and reviews. Strong adherence to the above-mentioned structure, working on the clarity factor of your proposal, makes it an attractive document for investors and leads toward the success of your venture. A business plan is a living document; it should be evolved with the business growth and time-changing market conditions. Periodic revision and updating of your business plan will remind you of long-term goals, as well as permit adjustment according to new opportunities and challenges.